THE IMPORTANCE OF EDUCATION IN ISLAM
History of science and technology
History of science and technology
For historical accounts of the development of science and technology, see history of science and history of technology.
History of science
Frontispiece of the "Rudolphine Tables" published by Johannes Kepler in 1627
Background[hide].
Theories and sociology Historiography Pseudoscience.
Early cultures Classical Antiquity Middle Ages Renaissance Scientific Revolution Romanticism
By culture.
African Byzantine Chinese Indian Medieval Islamic
Natural sciences.
Astronomy Biology Botany Chemistry Ecology Evolution Geology Geophysics Paleontology Physics
Mathematics.
Algebra Calculus Combinatorics Geometry Logic Probability Statistics Trigonometry
Social sciences.
Anthropology Economics Geography Linguistics Political science Psychology Sociology Sustainability
Technology.
Agricultural science Computer science Materials science Engineering
Medicine.

Human medicine Veterinary medicine Anatomy Neuroscience Neurology Nutrition Pathology Pharmacy
List-Class article Timelines Portal Portal Category Category
The history of Science and Technology (HST) is a field of history which examines how humanity's understanding of the natural world (science) and ability to manipulate it (technology) have changed over the centuries. This academic discipline also studies the cultural, economic, and political impacts of scientific innovati....
Histories of science were originally written by practicing and retired scientists, starting primarily with William Whewell, as a way to communicate the virtues of science to the public. In the early 1930s, after a famous paper given by the Soviet historian Boris Hessen, was focused into looking at the ways in which scientific practices were allied with the needs and motivations of their context. After World War II, extensive resources were put into teaching and researching the discipline, with the hopes that it would help the public better understand both Science and Technology as they came to play an exceedingly prominent role in the world. In the 1960s, especially in the wake of the work done by Thomas Kuhn, the discipline began to serve a very different function, and began to be used as a way to critically examine the scientific enterprise. At the present time it is often closely aligned with the field of science studies.
womens education in pakistan
Importance of women's education
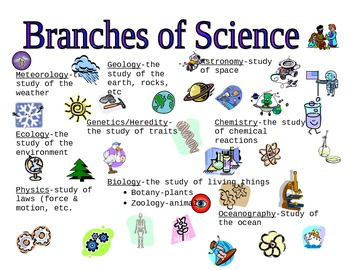
branches of science
Branches of Science
- a phenomenon in the physical world is observed
- an explanation, or hypothesis, for the phenomenon is formed
- the hypothesis is tested by means of objective, reproducible experiments
- Physical sciences, which deal with matter and energy and allow us to describe the material universe in terms of weight, mass, volume, and other standard, objective measures.
- Earth sciences, which explain the phenomena of Earth, its atmosphere, and the solar system to which it belongs.
- Life sciences, which describe living organisms, their internal processes, and their relationship to each other and the environment.

| Physical sciences | Life sciences | Earth sciences |
|---|---|---|
| Physics Kinetics Mechanics Electromagnetics Thermodynamics | Biology Botany Zoology | Geology Meteorology Astronomy |
| Chemistry Inorganic Chemistry Electrochemistry Analytical Chemistry | ||
| Examples of Overlapping Sciences | ||
| Physics + Chemistry = Physical Chemistry | Biology + Chemistry = Biochemistry Organic Chemistry | Geology + Chemistry = Geochemistry |
| Astronomy + Physics = Astrophysics | Biology + Geology = Paleontology | Geology + Astronomy = Astrogeology |
| Biology + Astronomy + Physics = Astronautics | ||
MACROMOLECULE
Macromolecule
Properties of carbon
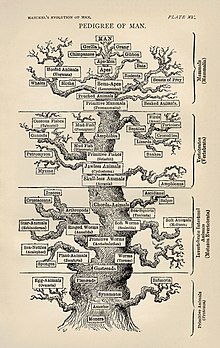
history of biology
History of biology
: History of biology
- The objects of our research will be the different forms and manifestations of life, the conditions and laws under which these phenomena occur, and the causes through which they have been effected. The science that concerns itself with these objects we will indicate by the name biology [Biologie] or the doctrine of life [Lebenslehre].
Structure of a cell
Structure of a cell

biology
| ||||
| Biology deals with the study of the many livingorganisms. (top: E. coli bacteria and gazelle) (bottom: Goliath beetle and tree fern) |